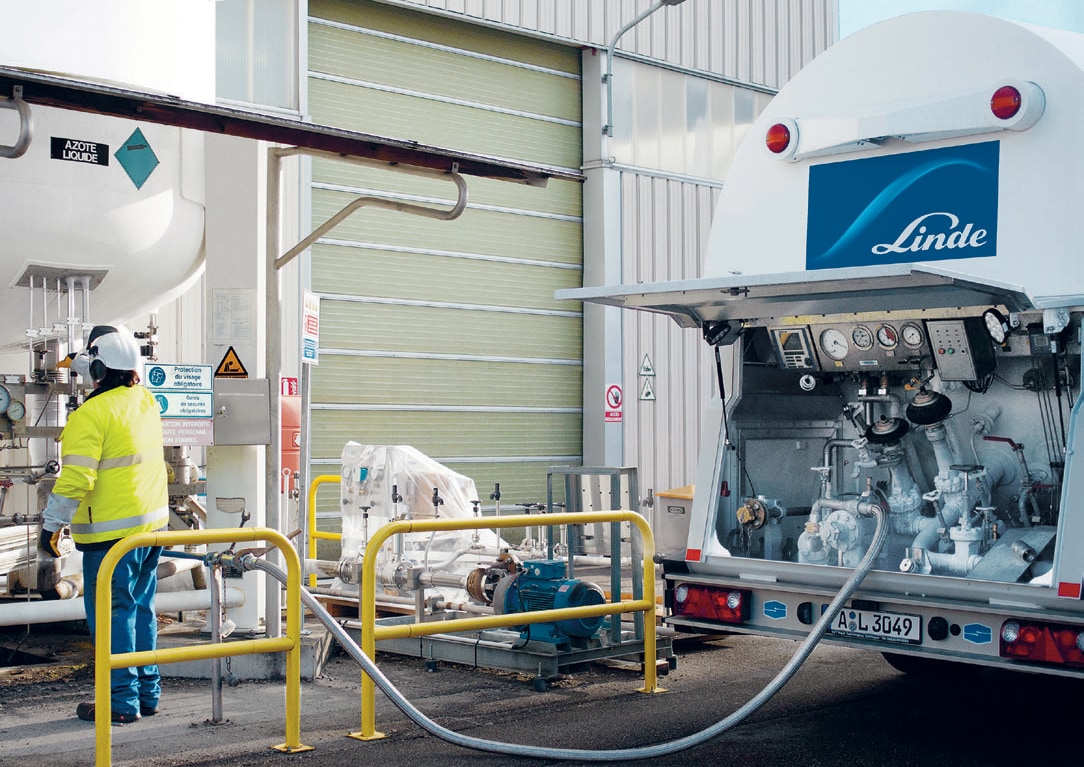
Secure production plants and food with inerting
There are many chemical processes where it is necessary to:
● prevent explosions
● eliminate unwanted reactions
● keep moisture away from products
● ensure safety during maintenance work
The basic principle of inerting is to replace the air around or above the product with dry inert gas,
forming a protective, safe gas layer over the substance that prevents oxygen and/or moisture from coming
into contact with reactive or absorbent substances. Additionally, inerting can be used for removing
flammable or toxic gases. An inert atmosphere is particularly important when storing highly volatile or
oxidizing products.
Inert gas does not directly interact with the compound or product. Nitrogen is the most commonly used gas
for this purpose, although carbon dioxide or argon are sometimes used as well.